11.classA {
12. public void process() { System.out.print(”A “); } }
13. class B extends A {
14. public void process() throws RuntimeException {
15. super.process();
16. if (true) throw new RuntimeException();
17. System.out.print(“B”); }}
18. public static void main(String[] args) {
19. try { ((A)new B()).process(); }
20. catch (Exception e) { System.out.print(”Exception “); }
21. }
What is the result?()
Class TestException
1. public class TestException extends Exception {
2. } Class a:
1. public class a {
2.
3. public String sayHello(String name) throws TestException {
4.
5. if(name == null) {
6. throw new TestException();
7. }
8.
9. return “Hello “+ name;
10. }
11.
12. }
A programmer wants to use this code in an application:
45. A a=new A();
46. System.out.println(a.sayHello(”John”));
Which two are true?()
Given:
11.String test = "Test A. Test B. Test C.";
12.// insert code here
13.String[] result = test.split(regex);
Which regular expression, inserted at line 12,correctly splits test into "Test A","Test B",and "Test C"?()
Which statements concerning the relationships between the following classes are true?()
class Foo { int num;
Baz comp = new Baz();
}
class Bar { boolean flag;
}
class Baz extends Foo {
Bar thing = new Bar();
double limit;
}
int index = 1;
boolean test = new Boolean;
boolean foo= test [index];
What is the result?()
String foo = “blue”;
Boolean[]bar = new Boolean [1];
if (bar[0]) {
foo = “green”;
}
What is the result? ()
数据库mydb中有关系表student,其结构如下:
student(sno学号,sname姓名,sex性别,birthday生日)
现编写一个学生信息浏览程序,设计界面和运行界面如下图所示:
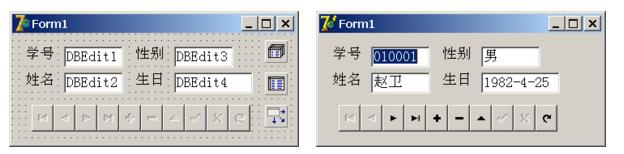
在下划线处填写相应数据库组件的属性值:
Database1. DatabaseName : mydb
Table1. DatabaseName : mydb T
able1. TableName : student
Table1. Active :(①)
Datasource1.DataSet :(②)
DBNavigator1. DataSource : (③)
DBEdit2. DataSource :(④)
DBEdit2. DataField :(⑤)
class java {
public static void main(String [] java) {
for (int Java = 1; Java 〈 java.length; Java++)
System.out.print("java ");
}
}
和命令行:
java java java java java
结果为:()
A typical example of a process # 19082 in the /proc file would be:
# ls -l /proc/19082
total 0
dr-xr-xr-x 1 root system 0 Sep 15 15:12 .
dr-xr-xr-x 1 root system 0 Sept 15 15:12 ..
-rw------- 1 root system 0 Sept 15 15:12 as
-r-------- 1 root system 128 Sept 15 15:12 cred
--w------- 1 root system 0 Sept 15 15:12 ctl
dr-xr-xr-x 1 root system 0 Sept 15 15:12 lwp
-r-------- 1 root system 0 Sept 15 15:12 map
dr-x------ 1 root system 0 Sept 15 15:12 object
-r--r--r-- 1 root system 448 Sept 15 15:12 psinfo
-r-------- 1 root system 1024 Sept 15 15:12 sigact
-r-------- 1 root system 1520 Sept 15 15:12 status
-r--r--r-- 1 root system 0 Sept 15 15:12 sysent
Writing to which of the following files will allow the owner to stop a process?()
You are designing a top-level OU structure to meet the business and technical requirements.
Which top-evel OU or OUs should you use? ()
Given:
12.Date date = new Date();
13.df.setLocale(Locale.ITALY);
14.String s = df.format(date);
The variable df is an object of type DateFormat that has been initialized in line 11.
What is the result if this code is run on December 14, 2000?()
public class TestOne {
public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(”sleep”);
}
}
What is the result?()
public class A extends Thread {
A() {
setDaemon(true);
}
public void run() {
(new B()).start();
try {
Thread.sleep(60000);
} catch (InterruptedException x) {}
System.out.println(“A done”);
}
class B extends Thread {
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(60000);
} catch (InterruptedException x) {}
System.out.println(“B done”);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
(new A()).start();
}
}
What is the result?()

Given:
11. public void genNumbers() {
12. ArrayList numbers = new ArrayList();
13. for (int i=0; i<10; i++) {
14. int value = i * ((int) Math.random());
15. Integer intObj = new Integer(value);
16. numbers.add(intObj);
17. }
18. System.out.println(numbers);
19. }
Which line of code marks the earliest point that an object referenced by intObj becomes a candidate for garbage collection?()
11. public void genNumbers() {
12. ArrayList numbers = new ArrayList();
13. for (int i=0; i<10; i++) {
14. int value = i * ((int) Math.random());
15. Integer intObj = new Integer(value);
16. numbers.add(intObj);
17. }
18. System.out.println(numbers);
19. }
Which line of code marks the earliest point that an object referenced by intObj becomes a candidate for garbage collection?()
public class Car {
private int wheelCount;
private String vin;
public Car(String vin) {
this.vin = vin;
this.wheelCount = 4;
}
public String drive() {
return “zoom-zoom”;
}
public String getInfo() {
return “VIN: “+ vin + “wheels: “+ wheelCount;
}
}
And:
public class MeGo extends Car {
public MeGo(String vin) {
this.wheelCount = 3;
}
}
What two must the programmer do to correct the compilation errors?()
1. class Pizza {
2. java.util.ArrayList toppings;
3. public final void addTopping(String topping) {
4. toppings.add(topping);
5. }
6. }
7. public class PepperoniPizza extends Pizza {
8. public void addTopping(String topping) {
9. System.out.println(”Cannot add Toppings”);
10. }
11. public static void main(String[] args) {
12. Pizza pizza = new PepperoniPizza();
13. pizza.addTopping(”Mushrooms”);
14. }
15. }
What is the result?()
public class X {
public static void main (String[]args) {
string s = new string (“Hello”);
modify(s);
System.out.printIn(s);
}
public static void modify (String s) {
s += “world!”;
}
}
What is the result?()
分析下列Java代码:
class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
method(); }
static void method() { try {
System.out.println("Hello"); System.exit(0); }
finally {
System.out.println("good-bye"); } } }
编译运行后,输出结果是()。
1. public class SimpleCalc {
2. public int value;
3. public void calculate() { value += 7; }
4. }
And:
1. public class MultiCalc extends SimpleCalc {
2. public void calculate() { value -= 3; }
3. public void calculate(int multiplier) {
4. calculate();
5. super.calculate();
6. value *=multiplier;
7. }
8. public static void main(String[] args) {
9. MultiCalc calculator = new MultiCalc();
10. calculator.calculate(2);
11. System.out.println(”Value is: “+ calculator.value);
12. }
13. }
What is the result?()
What is wrong with the following code?()
class MyException extends Exception {}
public class Qb4ab {
public void foo() { try { bar(); } finally { baz();
} catch (MyException e) {}
}
public void bar() throws MyException {
throw new MyException();
}
public void baz() throws RuntimeException {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
class Birds {
public static void main(String [] args) {
try {
throw new Exception();
} catch (Exception e) {
try {
throw new Exception();
} catch (Exception e2) { System.out.print("inner "); }
System.out.print("middle ");
}
System.out.print("outer ");
}
}
结果为:()
现有:
class Birds {
public static void main (String [] args) {
try {
throw new Exception () ;
} catch (Exception e) {
try {
throw new Exception () ;
} catch (Exception e2) { System.out.print ("inner "); }
System. out.print ( "middle" ) ;
}
System.out.print ("outer") ;
}
}
结果是()
Given:
11. static class A {
12. void process() throws Exception { throw new Exception(); }
13. }
14. static class B extends A {
15. void process() { System.out.println("B "); }
16. }
17. public static void main(String[] args) {
18. A a = new B();
19. a.process();
20. }
What is the result? ()
public class Test {
public static void aMethod() throws Exception {
try {
throw new Exception();
} finally {
System.out.println(“finally”);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
aMethod();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(“exception”);
}
System.out.println(“finished”);
}
}
What is the result?()
现有:
void topGo() {
try {
middleGo();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.print("catch");
}
}
void middleGo() throws Exception {
go();
system.out.print("late middle");
}
void go() throws ExceptiOn {
throw new Exception();
}
如果调用 topGo () ,则结果为:()
11. static class A {
12. void process() throws Exception { throw new Exception(); }
13. }
14. static class B extends A {
15. void process() { System.out.println(”B”); }
16. }
17. public static void main(String[] args) {
18. new B().process();
19. }
What is the result?()
11. static classA {
12. void process() throws Exception { throw new Exception(); }
13. }
14. static class B extends A {
15. void process() { System.out.println(”B “); }
16. }
17. public static void main(String[] args) {
18.A a=new B();
19. a.process();
20.}
What is the result?()
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExceptionTest(
public static void main (Stringargs)
try (
methodA();
) catch (IOException e) (
system.out.printIn(“Caught IOException”);
) catch (Exception e) (
system.out.printIn(“Caught Exception”);
)
)
public void methodA () {
throw new IOException ();
}
What is the result?()
1. class Exc0 extends Exception { }
2. class Exc1 extends Exc0 { }
3. public class Test {
4. public static void main(String args[]) {
5. try {
6. throw new Exc1();
7. } catch (Exc0 e0) {
8. System.out.println(“Ex0 caught”);
9. } catch (Exception e) {
10. System.out.println(“exception caught”);
11. }
12. }
13. }
What is the result?()
现有:
class ThreadExcept implements Runnable {
public void run() { throw new RuntimeException("exception "); }
public static void main(String [] args) {
new Thread(new ThreadExcept()).start();
try {
int x = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
Thread.sleep(x);
System.out.print("main ");
} catch (Exception e) { }
}
}
和命令行:
java ThreadExcept 1000
哪一个是结果?()
11.classA {
12. public void process() { System.out.print(”A “); } }
13. class B extends A {
14. public void process() throws RuntimeException {
15. super.process();
16. if (true) throw new RuntimeException();
17. System.out.print(“B”); }}
18. public static void main(String[] args) {
19. try { ((A)new B()).process(); }
20. catch (Exception e) { System.out.print(”Exception “); }
21. }
What is the result?()
11.classa {
12. public void process() { System.out.print(”a,”); } }
13. class b extends a {
14. public void process() throws IOException {
15. super.process();
16. System.out.print(”b,”);
17. throw new IOException();
18. } }
19. public static void main(String[] args) {
20. try { new b().process(); }
21. catch (IOException e) { System.out.println(”Exception”); } }
What is the result?()
免费的网站请分享给朋友吧